1 TF-IDF
- 使用 TF-IDF 进行特征词的选取,将所有文章转化成特征词 TF-IDF 矩阵
1
2vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer ( max_df=0.95,max_features=20000, min_df=2, use_idf=True )
X = vectorizer.fit_transform ( texts ) - TF-IDF 原理
假设有一篇文章一共有 100 个词,其中「卫浴」、「九牧」分别出现了 100 和 40 次,那么它们的词频分别如下:
假设语料库中一共有 50 篇文章,其中包含「卫浴」的文章有 19 篇,包含「九牧」的有 9 篇,那么它们的 IDF 计算如下:
TF-IDF 的计算结果如下:
- TF-IDF 优缺点
TF-IDF 的优点是简单快速,而且容易理解。缺点是有时候用词频来衡量文章中的一个词的重要性不够全面,有时候重要的词出现的可能不够多,而且这种计算无法体现位置信息,无法体现词在上下文的重要性。[reference: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/31197209]
2 K-means
- 使用 K-means 进行文本聚类
k-means 算法需要事先指定簇的个数 k,算法开始随机选择 k 个记录点作为中心点,然后遍历整个数据集的各条记录,将每条记录归到离它最近的中心点所在的簇中,之后以各个簇的记录的均值中心点取代之前的中心点,然后不断迭代,直到收敛


- K-means 优缺点
容易理解,而且有效,但是计算量比较大,耗费时间长,K 的个数不好确定
3 TextRank
提到 TextRank,我们需要先从 PageRank 说起
- 3.1 PageRank
PageRank,又称网页排名、谷歌左侧排名,是一种由搜索引擎根据网页之间相互的超链接计算的技术,而作为网页排名的要素之一,以 Google 公司创办人拉里·佩奇 ( Larry Page ) 之姓来命名。
假设一个由 4 个网页组成的群体:A, B,C 和 D。如果所有页面都只链接至 A,那么 A 的 PR ( PageRank ) 值将是 B, C 及 D 的 Pagerank 总和。
![] ( https://wx2.sinaimg.cn/mw690/e59539f0ly1g1jhnsn7wxj208a07zt8q.jpg )
计算公式如下:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762247287744613.png )
重新假设 B 链接到 A 和 C, C 只链接到 A,并且 D 链接到全部其他的 3 个页面。一个页面总共只有一票。所以 B 给 A 和 C 每个页面半票。以同样的逻辑,D 投出的票只有三分之一算到了 A 的 PageRank 上。
![] ( https://wx3.sinaimg.cn/mw690/e59539f0ly1g1jho6s18cj207u07swek.jpg )
计算公式如下:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762238832115527.png )
- 3.1.1 计算公式
对于一个页面 A,那么它的 PR 值为:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762264513765890.png )
PR ( A ) 是页面 A 的 PR 值
PR ( Ti ) 是页面 Ti 的 PR 值,在这里,页面 Ti 是指向 A 的所有页面中的某个页面
C ( Ti ) 是页面 Ti 的出度,也就是 Ti 指向其他页面的边的个数
d 为阻尼系数,其意义是,在任意时刻,用户到达某页面后并继续向后浏览的概率,该数值是根据上网者使用浏览器书签的平均频率估算而得,通常 d=0.85>d 是个经验值。在 0.85 的阻尼系数下,大约 100 多次迭代就能收敛到 PR 向量。当阻尼系数接近 1 时,需要的迭代次数会陡然增加很多,且排序不稳定。
3.1.2 具体实例
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762159949967486.png )
三个页面 A、B、C 为了便于计算,我们假设每个页面的 PR 初始值为 1, d 为 0.5。
- 页面 A 的 PR 值计算如下:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762153669456933.png )
- 页面 B 的 PR 值计算如下:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762147268488165.png )
- 页面 C 的 PR 值计算如下:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762141558183138.png )
下面是迭代计算 12 轮之后,各个页面的 PR 值:
![] ( https://www.quantinfo.com/attachment/article/20180728/1532762134982268920.jpg )
那么什么时候,迭代结束哪?一般要设置收敛条件:比如上次迭代结果与本次迭代结果小于某个误差,我们结束程序运行;比如还可以设置最大循环次数。
- 3.1.3 代码实现
1 | import numpy as np |
阅读原文: PageRank 算法原理与实现
- 3.2 TextRank
TextRank 将某一个词与其前面的 N 个词、以及后面的 N 个词均具有图相邻关系 ( 类似于 N-gram 语法模型 ) 。具体实现:设置一个长度为 N 的滑动窗口,所有在这个窗口之内的词都视作词结点的相邻结点;则 TextRank 构建的词图为无向图。下图给出了由一个文档构建的词图 ( 去掉了停用词并按词性做了筛选 ) :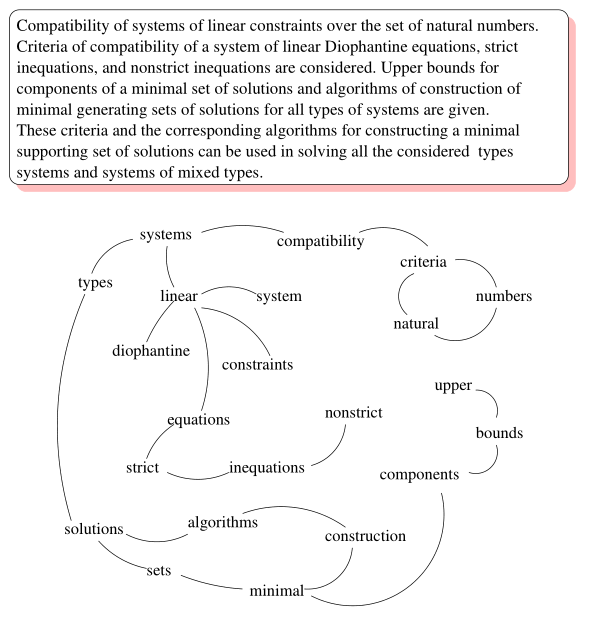
考虑到不同词对可能有不同的共现 ( co-occurrence ) ,TextRank 将共现作为无向图边的权值。那么,TextRank 的迭代计算公式如下:
![] ( https://www.letiantian.me/content/images/2014/12/textrank-02.png )
原文链接: